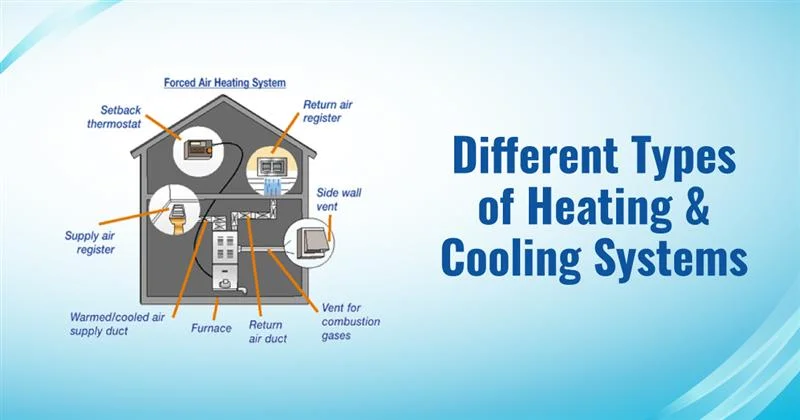
The system you pick to heat and cool your home matters a lot. It doesn’t just control how warm or cool your space feels—it also plays a major role in your energy bills. In fact, heating and cooling can make up more than half of your home’s energy use every year. That means the system you install could help you save a lot of money over time. But it’s not just about the cost. A good heating and cooling system also keeps your home comfortable in every season, with the right temperature and humidity levels to match your needs. The right setup can improve sleep, protect your furniture, and even support your health.
Many heating and cooling systems are built to last for 10 to 20 years, so this isn’t a choice you make often. That’s why it’s worth taking the time to learn about the different types available. Each system comes with its own pros and cons, and not every option will suit every home. By understanding how these systems work—and what makes each one different—you’ll be better prepared to make the best choice for your house, your budget, and your comfort.
Why Does the Heating and Cooling System Matter?
A comfortable home starts with the right heating and cooling setup. It helps manage more than just the indoor temperature. It impacts how you feel, your well-being, and what you pay for energy. A good system keeps your home cool in summer and warm in winter. It also controls humidity and improves air quality, stopping dampness and cutting down on allergens.
The right heating and cooling systems also make your home more energy-efficient. If your system is outdated or the wrong type for your space, you may waste a lot of energy, which leads to high utility bills. Choosing the best system for your home ensures you’re not paying more than you need to.
Tips to Consider When Choosing a System:
- Think About the Size of Your Home: Big homes may work better with central or ducted heating and cooling systems. Small homes can often use split systems or portable units.
- Climate Matters: Evaporative cooling works well in hot places. Gas ducted heating is often better for cold areas.
- Energy Efficiency: Look for energy-efficient models. They may cost more upfront but save you money over time by using less power.
- Maintenance Requirements: Some systems need more regular maintenance than others. Be sure you’re comfortable with how much care a system requires before you commit.
- Budget: Think about the installation cost and the cost to run the system. Some are cheap to install but cost more to use.
Choosing the right system isn’t just about what’s popular. It’s about what works best for your home, your needs, and your budget. If you know how different systems work, you can pick one that keeps you comfortable and saves you money for years.
Different Ways to Heat and Cool Your Home
There are several ways to heat and cool your home, and choosing the right system can make a big difference in both comfort and energy efficiency. Whether you’re trying to stay warm in the winter or cool in the summer, it’s important to consider the size of your home, your budget, and the climate in your area. Each system works a little differently, and what works best for one home may not be ideal for another. Below, we’ll explore some of the most common heating and cooling options available, so you can find the one that fits your needs.
Electric Systems
Most home air conditioners come with an Energy Rating Label. This label shows the system’s efficiency in three different climate zones: hot, average, and cold. It’s called a Zoned Energy Rating Label and helps you choose a product that’s right for your area.
Solar panels can help you save money. They are cheap and good for the planet. You can use solar batteries to store energy for later. These batteries are getting cheaper, too.
Gas Systems
Gas heaters also come with an energy rating label before they are sold. This label is part of a certification process required by gas safety regulators. The efficiency of gas heaters varies. Some lose heat through the flue, while others lose heat through open windows.
Unflued gas heaters are not very good at keeping heat in. They need electricity to run fans and parts, which makes them cost more to use.
Types of Cooling Systems
Cooling systems are essential for keeping your home comfortable in hot weather. Here are some of the most common types of cooling systems for homes:
1. Fans
Fans are a common and budget-friendly option for staying cool. They don’t lower the temperature of a room, but they can make you feel cooler by moving air around. Fans can reduce the perceived temperature by about 3°C, making a big difference on hot days.
To get the full cooling effect, the fan needs to blow air directly on you. While fans are affordable to buy, they are also very cheap to run, costing only around 2 cents per hour. Fans are perfect for smaller spaces or for supplementing other cooling systems.
2. Reverse-Cycle Air Conditioners (Heat Pumps)
Heat pumps, or reverse cycle air conditioners, can heat and cool your home. They save energy and money. They work well all year.
- Efficient Heating and Cooling: During summer, they help cool your home by pushing out warm air. In winter, they bring outdoor heat inside to warm your space.
- All-Season Solution: You don’t need separate systems for cooling and heating. A reverse cycle unit does it all.
- Energy Savings: These systems use less power than regular heaters. This helps you save money on energy bills.
- Zone Control: Some models can heat or cool just one room. This saves energy by only using power where it is needed.
- Environmentally Friendly: Reverse cycle systems make less greenhouse gas. They move heat instead of making it.
3. Portable Air Conditioners
Cooling a space without a complex setup? Portable units can do the job. They can be moved from room to room, but they tend to be noisy and less efficient than fixed units. They require an exhaust duct, which must be placed through an open window. Portable air conditioners mostly use a lot of power. They don’t save much energy.
4. Evaporative Coolers
Evaporative coolers work well in dry, low-humidity areas. They cool air by passing it over water-soaked filters, then blow the cooled air into the house while pushing out hot air through open windows.
Tips for Using Evaporative Coolers:
- Best for Dry Areas: They’re most effective in low-humidity regions.
- Energy Efficient: Ducted models use less power than air conditioners.
- Watch Water Usage: They consume up to 25 liters per hour.
- Ensure Ventilation: Open windows to let warm air out for better cooling.
- Inverter Models: Choose inverter-driven fans for better energy savings.
- Portable Limitations: Portable units work best in dry areas with good airflow.

Types of Heaters to Warm Up Your Space
When the weather turns cold, having the right heating system can make all the difference in staying comfortable. There are various types of heaters to choose from, each designed to suit different spaces and needs. Whether you’re looking for an energy-efficient option or something portable for smaller rooms, the right heater can help you stay warm without breaking the bank. Let’s take a look at some popular heater types and their benefits.
1. Gas Heaters
Gas heaters are a popular choice for heating homes due to their efficiency and ability to quickly warm up a space. They come in various styles, making them suitable for different room sizes and heating needs. Gas-powered heating is often more affordable to run compared to electric heaters, especially for larger spaces. Let’s explore the different types of gas heaters and their benefits.
Ducted Gas Heating
Ducted gas heaters are installed under the floor, in the ceiling, or near an external wall. Heat is spread through ducts in the ceiling or floor, warming the whole home. These systems are effective but can be costly to run, as they use a lot of gas and electricity for the fans.
Ducted gas heating costs a lot to set up and run. But you can heat only the rooms you use. Cleaning filters and regular check-ups help it work well. A licensed technician should service it.
For comfort all year, you can use ducted gas heating with an evaporative cooler. But a reverse-cycle air conditioner may be a better choice.
Tip: To save on running costs, use zoning to heat only the rooms in use.
Portable Gas Heaters
Portable gas heaters don’t have a vent to send gases outside. Some places don’t allow them because they can be unsafe. These heaters release carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and water vapour. They also use up the room’s oxygen.
Unflued gas heaters need good airflow to be safe, like an open window. If there isn’t enough air, they don’t work as well, especially on very cold days.
Tip: Always keep a window open when using unflued gas heaters to stay safe.
Flued Gas Heaters
Flued gas heaters are safer than portable models because they vent gases outside the home. There are two main types:
Open-flued heaters use air from the room. They need vents to work safely. This can make them less efficient, especially when it’s very cold.
Room-sealed flued heaters are the safest and most efficient. They don’t use room air and don’t need extra ventilation. These models cost more to buy and install but offer better safety and performance.
Open-flued heaters still raise safety concerns and must be used with proper airflow to avoid risks.
Tip: Choose room-sealed models for better safety and fewer ventilation needs.
2. Electric Heaters
Electric heaters are a common way to warm up homes, especially smaller spaces. They are also called electric resistance heaters. These systems work by converting electricity directly into heat using a heating element. Most electric heaters are portable, but some are fixed in place. While they are 100% efficient at turning power into heat, they can be costly to run for long periods. Let’s look at the different types of electric heaters and how they work.
Fan Heaters
Fan heaters use convection to warm the air, with a fan pushing the heat out. They heat up quickly and are best for small spaces. Some larger models can warm up an entire room, but they may be noisier and use more energy.
Tip: Use fan heaters for short bursts of heat in small, enclosed spaces.
Oil-Filled Heaters
Oil-filled heaters use both radiant and convective heat. The oil inside heats up and spreads warmth through the unit and into the room. The oil is sealed inside, so it never needs refilling or replacing. These heaters are quiet, safe, and have a lower surface temperature. The heating element is hidden, reducing burn risks. Some models include a fan for faster room heating.
Tip: Use oil-filled heaters in bedrooms or quiet areas for gentle, steady warmth.
Radiant Heaters
Radiant heaters warm people and objects directly, not the air around them. They are ideal for small rooms or large cold spaces where you need direct heat. A common type is the bar heater, which gives off strong, focused warmth.
Tip: Use radiant heaters where quick, direct heat is needed—like near your work desk or couch.
Heat Lamps
Heat lamps are mostly used in bathrooms. They give quick, direct heat and are perfect for short use, like after a shower. These lamps warm you, not the whole room.
Tip: Use heat lamps only when needed to save energy.
3. Other Heating Options
Not all heating systems are regular heaters. Some help make your home warmer in other ways.
Heat Shifters
Heat shifters move warm air from heated rooms to colder ones using a fan and ducting. They don’t create heat but help spread it. These are low-cost and easy to run.
Tip: Use heat shifters to make the most of existing heat without extra energy use.
Hydronic Radiant Heating
These systems use hot or cold liquid, flowing through wall panels or pipes in the floor, to heat or cool rooms. They’re quiet and clean since they don’t blow air or dust. Though costly to install, they’re cheaper to run with solar power or heat pumps.
Tip: Pair with solar or an electric heat pump for lower long-term costs.
Wood Heaters
Modern wood heaters, like slow combustion models, are more efficient and cleaner than open fires or pot-belly stoves. Open flames use room oxygen and need ventilation, which lowers heat output. Wood smoke can cause pollution, and some areas restrict wood heater use.
Tip: Check local rules before installing a wood heater to avoid fines or limits.
Need Help Choosing? Talk to a Pro
Finding the right heating and cooling system isn’t always simple. Each home has different needs based on size, layout, insulation, and location. Every home is different, so one solution won’t fit all. That’s why it’s smart to speak with a licensed professional before making a decision.
An expert can help you compare the different types of heating and cooling systems for homes. They’ll explain which options fit your climate, your energy usage, and your budget. They can also recommend systems that work well with solar or energy-efficient upgrades.
Getting professional help can save money. If a system is too big or too small, it won’t work well and could raise your power bills. A trained installer will fit the system correctly. This makes it safer, more comfortable, and uses less energy.
Final Thoughts
There are many types of heating and cooling systems, each with its own pros and cons. What works for one home may not suit another, so it’s important to choose the right option for your needs, space, and budget. A well-chosen system can keep your home comfortable all year while helping you save on energy costs.
Still not sure what’s best for your home? You don’t have to figure it out alone. Contact Answer Air Services today—our friendly, trained technicians can assess your space and recommend the best heating and cooling solution. From reverse-cycle air conditioners to ducted gas systems, we’ll help you stay warm in winter and cool in summer.